Propranolol competes with sympathomimetic neurotransmitters such as catecholamines for binding at beta(1)-adrenergic receptors in the heart, inhibiting sympathetic stimulation. This results in a reduction in resting heart rate, cardiac output, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and reflex orthostatic hypotension.
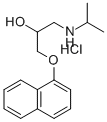
Propanolol Hcl
| Description | |
|---|---|
| (RS)-1-(isopropylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)propan-2-ol | |
| 318-98-9 | |
| C16H22CINO2 | |
| (RS)-1-[(1-METHYLETHYL)AMINO]-3-(1-NAPHTHALENYLOXY)-2-PROPANOL HYDROCHLORIDE;PROPRANOLOL HCL;(+/-)-PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE;PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE;(+/-)-PROPANOLOL HCL;PROPANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE;1-((1-methylethyl)amino)-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-2-propanohydrochloride;1-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-hydroxy-3-isopropylaminopropanehydrochloride | |
| For the prophylaxis of migraine | |
