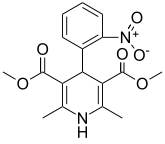
Nifedipine has been formulated as both a long- and short-acting 1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. It acts primarily on vascular smooth muscle cells by stabilizing voltage-gated L-type calcium channels in their inactive conformation. By inhibiting the influx of calcium in smooth muscle cells, nifedipine prevents calcium-dependent myocyte contraction and vasoconstriction. A second proposed mechanism for the drug’s vasodilatory effects involves pH-dependent inhibition of calcium influx via inhibition of smooth muscle carbonic anhydrase. Nifedipine is used to treat hypertension and chronic stable angina.
Nifedipine
| Description | |
|---|---|
| 3,5-dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | |
| 21829-25-4 | |
| C17H18N2O6 | |
| Orix;Oxcord;ADALAT;Anifed;bay1040;Nifedin;Nifelan;Pidilat;Sepamit;Zenusin | |
| For the management of vasospastic angina, chronic stable angina, hypertension, and Raynaud's phenomenon. May be used as a first line agent for left ventricular hypertrophy and isolated systolic hypertension (long-acting agents). | |
